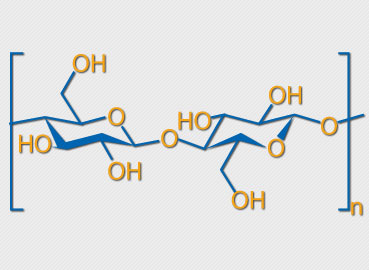
What is cellulose
Cellulose is a long chain of linked sugar molecules that gives wood its remarkable strength. It is the main component of plant cell walls,
and the basic building block for many textiles and for paper. Cotton is the purest natural form of cellulose. In the laboratory, ashless filter paper is a source of nearly pure cellulose.
Cellulose is a natural polymer, a long chain made by the linking of smaller molecules. The links in the cellulose chain are a type of sugar: ß-D-glucose. Two unlinked molecules of ß-D-glucose are pictured at right 1. The sugar units are linked when water is eliminated by combining the -OH group and H highlighted in gray. Linking just two of these sugars produces a disaccharide called cellobiose 2. Cellulose is a polysaccharide produced by linking additional sugars in exactly the same way. The length of the chain varies greatly, from a few hundred sugar units in wood pulp to over 6000 for cotton.
The cellulose chain bristles with polar -OH groups. These groups form many hydrogen bonds with OH groups on adjacent chains, bundling the chains together. The chains also pack regularly in places to form hard, stable crystalline regions that give the bundled chains even more stability and strength.
Cellulose is a major component of wood. Cellulose fibers in wood are bound in lignin, a complex polymer. Paper-making involves treating wood pulp with alkalis or bisulfites to disintegrate the lignin, and then pressing the pulp to matte the cellulose fibers together.
Cellulose is found in large amounts in nearly all plants, and is potentially a major food source. Unfortunately, human beings lack the enzymes necessary to cleave the linkages between the sugars in cellulose. In fact, crystallite cellulose is added to some foods to reduce the caloric value.
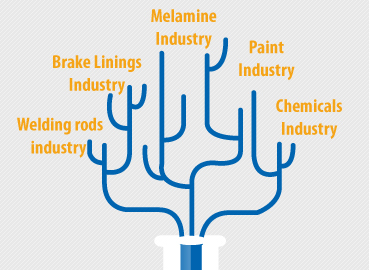
What Is Cellulose Used For
Cellulose is a natural material created cotton linter or wood pulp conceder as main raw materials to produce many products such as
wilding electrode production
Filtration of oils to catch the fatty materials
Paint production companies in decorative and cracks batty
Using in special cement mixture in modern chemical building companies
Production of cellulosic thickeners such as CMC HEC
Car break materials as coolant filler
Melamine production materials as filler
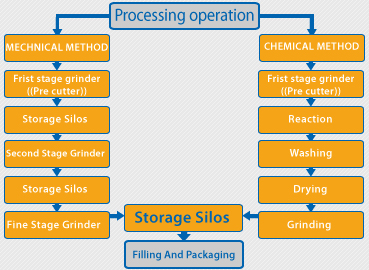
Processing operation
The manufacturing of cellulose powder and fibers were classified into two main technologies
Mechanical technology
This technology based on the mechanical disintegration of pure Alfa cellulose, using high modified malty stage grinders silo storing system
Chemical technology
This technology based on chemical reaction by adding some chemicals in especial vessels well sealed under certain pressure and temperature
the main significance of this method is to decomposed the small articles which is normally grown in the outer surfaces of the fibers and response for attach the fibers with each other formed accumulation of fibers

